Earth’s Orbit
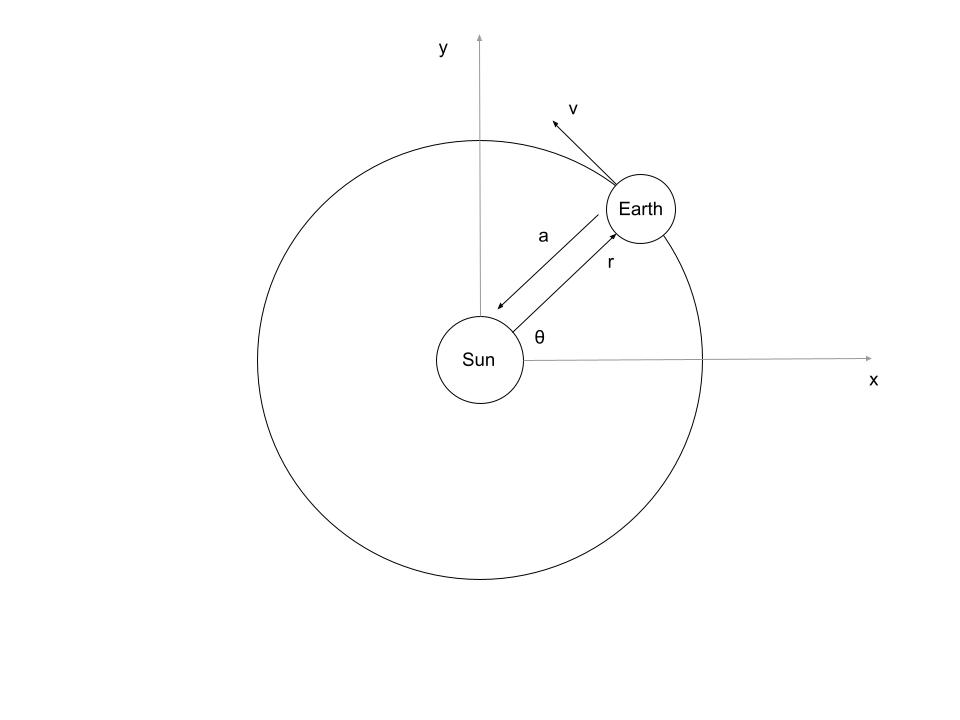
Earth has uniform circular motion. We will use the above scenario for all of our derivations below.
Position
We define the radius vector of Earth relative to the sun
or
where
The period is
Velocity
To find velocity,
Note that , meaning velocity and radius are perpendicular.
This means speed, angular frequency, and radius are related independent of time.
Acceleration
Note that acceleration and radius are antiparallel.
Force
Let
is called the unit vector of .
We can rewrite
Example: Two Masses through Hole in Table
Consider.

Then,
This relationship is one of Kepler’s Laws.
Example: Earth (again)
Assuming Earth’s orbit ~ uniform circular motion.
also,
means farther out period longer, weaker gravity period longer.
If you hypothetically had asteroids parallel to Earth, then they would not move in sync because farther out means slower.
However, there are Lagrange Points, for which asteroids would move in sync to Earth. This is because if asteroid and Earth are aligned with sun, the increased gravity between asteroid and Earth will increase .
Another conjecture about how Moon formed: some massive body collided with Earth, debris became moon.