Organic Chemistry
- study of carbon containing compound
- carbon has great properties for being building block framework
- can accumulate charge
- Pauline Electronegativity is intermediate
Alkanes
- n-alkanes
- cyclic alkanes
- branched-chain
Normal Alkanes
- also called straight-chain, -alkanes
- all C-H or C-C bonds, fully saturated
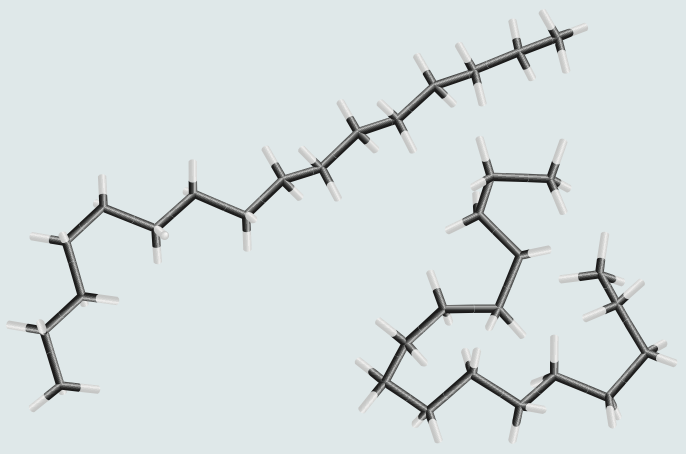
- all C are bonded to <2C
- all are tetrahedral +

Cyclic Alkanes
- cycloalkane: one chain of attached at ends to form loop

- name: straight chain name + cyclo- at front
- chair conformation:

- boat conformation:

Branched-Chain Alkanes
- hydrocarbon only containing and single bonds
- 1+ carbon atoms in each molecule is bonded to 3/4 other carbon atoms
- allows for geometrical isomers
- butane and 2-methylpropane:
- also allows chirality (optical isomerism)
- one carbon 4 different atoms can have mirror images that are not superimposable

- connection to life: gas at gas station has “octane number”
- branched-chain and cycloalkanes combusts smoothly
- straight-chain alkanes burn unevenly, create knocking that could damge engine
- octane number based on this
Nomenclature
- named after longest continuous chain
- group attached to chain is named as -yl vs -ane
- long chain is named to substituent is the lowest number
- alkyl group of same type use di, tri, etc…
- several types of alkyl groups, name alphabetically
Rules for Shorthand
- all carbons are vertices or points
- each line is bond
- assume all are at octet
Alkenes and Alkynes
-
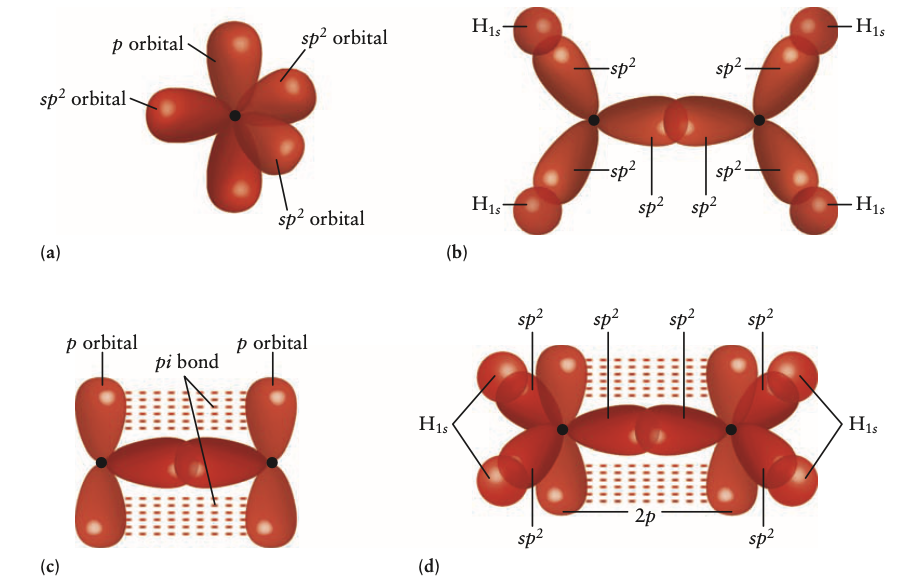
unsaturated carbon, carbon has double and triple bonds
-
alkene: double bond
- simplest: , ethene
- bonding shown below
-
- naming: replace -ane in corresponding alkane with -ene
- can have isomeric forms depending on position of bonding groups
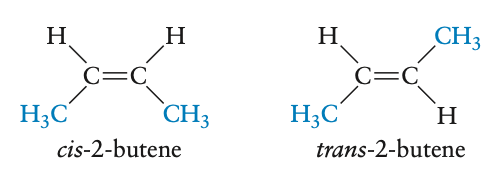
- polyenes: alkenes with multiple double bonds
- dienes have 2 double bonds, trienes have 3, etc…
- double bonds lead to cis and trans conformations
- examples:

- alkyne: triple bond
- simplest: , ethyne/acetylene
- naming: replace -ane in corresponding alkane with -yne
- bonding shown below

Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- hexagonal ring of carbon
- simplest example: benzene

- all bonds (single and double) actually have same length
- 6 orbitals 6 molecular orbitals
Connection to Real Life
- unsaturated/saturated/cis/trans are also how we described fats (fatty acids)
- saturated and trans unsaturated fats are unhealthy because of compound shape
- strong bonding solid at room temperature, thus clogs arteries
Connection to Human Health (Januvia)
- Januvia: drug that treats diabetes
- API: Sitagliptin
- unfortunately contained carcinogen from orgo chem reaction used to reduce waste