Periodic Table
- combines like elements together
- like = similar electron configurations in Atoms
- columns are groups
- rows are periods
- organizes elements into families
- similar chemical properties
- arranged with increasing atomic number (z)
- different ways to categorize
- metals, nonmentals, metalloids
- transition metals, main group, noble gases
- alkali, alkaline-earth, chalcogens, halogens, lanthanides, actinides
- tells us how electrons are arranged for each element
- as atomic number goes up, so does number of electrons
- trends are based on [[Electrons in Atoms#Quantum Numbers#Electron Configurations|similar electron configurations]]
Periodic Trends
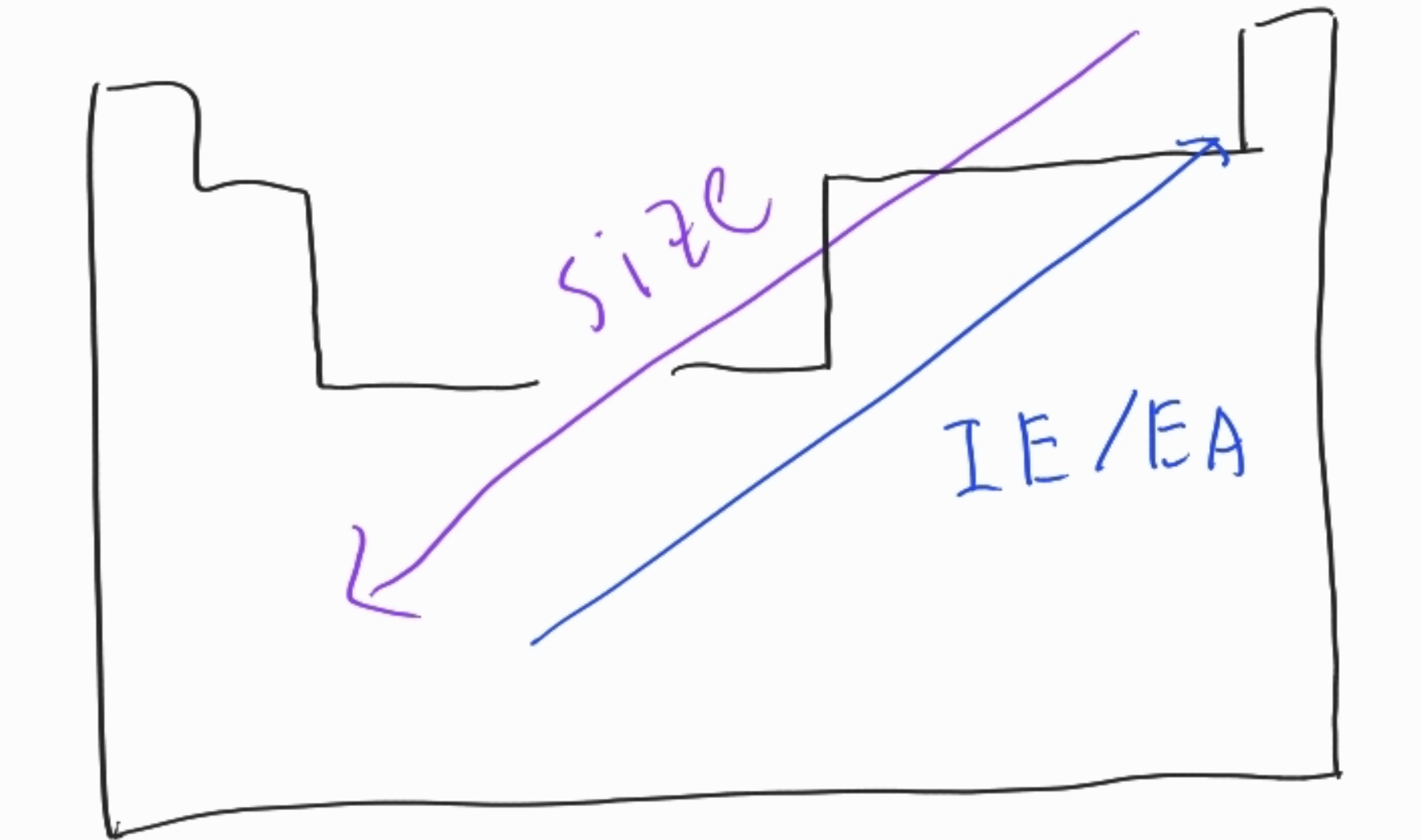
Size (Radial)
- impacts reactivity, physical properties
- electron energy
- includes electrons
- electron cloud is times larger than nucleus
- INCREASES WHEN
- GOING DOWN
- increases in principle quantum number
- GOING LEFT
- going right adds electrons to same valence
- effective nuclear charge remains same going to the right
-
- increases because increase in protons
- (screening constant) because only adding core electrons increases screening
-
- GOING DOWN
Ionization Energy
- INCREASES WHEN
- going UP
- going RIGHT
Electron Affinity
- INCREASES WHEN
- going UP
- less
- going RIGHT
-
elements like Li and K can become noble gas if giving away electron
-
- going UP
Electronegativity
- INCREASES WHEN
- going UP
- going RIGHT