Background §
- atomic orbitals are purely mathematical constructs
- only genuine wavefunction we know is in one electron system
- orbitals in multi-electron systems are approx
- atomic orbitals = basis set
Hybridization §
- hybridization: useful mathematical manipulation of orbitals to describe behavior of the second period in Bonds
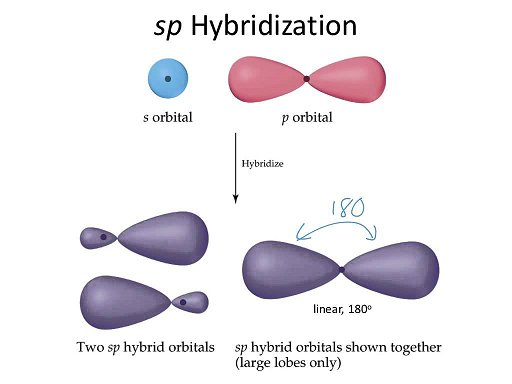
- 3 types; sp, sp2, sp3
- π represents hybrid orbitals
- ex1: BeH2 has linear geo, use hybridization to understand
- basis set: 1s, 2s, 2p
- valence: 2s, 2p
- px,py,pz
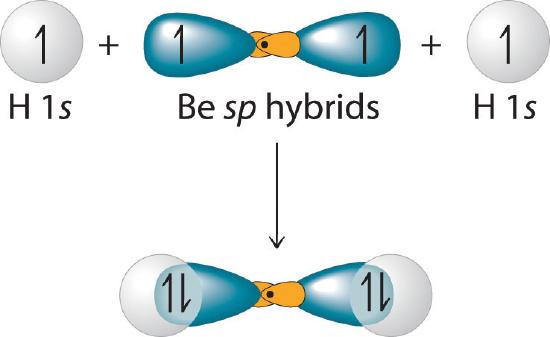
- mix 2s and 2pz
- π1(r)=C(−2s−2pz)
- π2(r)=C(−2s+2pz)

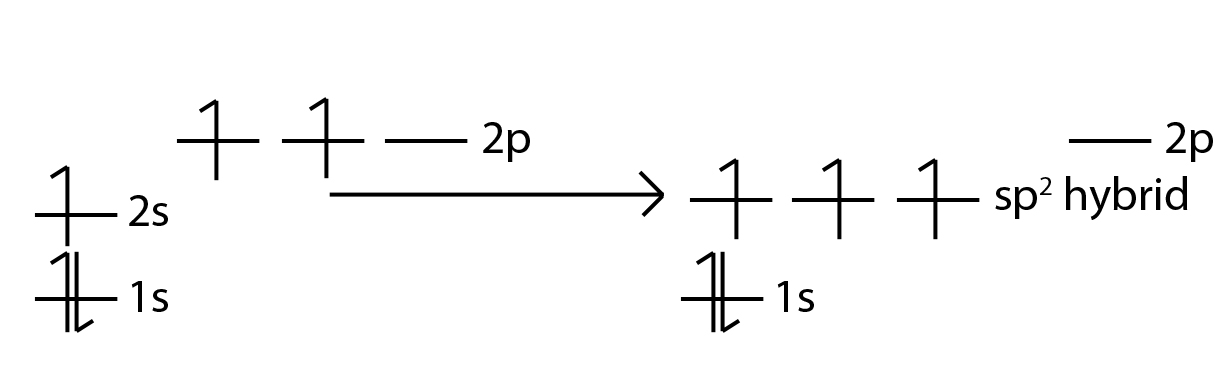
- BH3
- trigonal planar geo
- basis set: 2s,2px,2py,2pz
- π2(r)=(31)1/2(−2s)+2(61)1/2(2px)
- π1(r)=(31)2(−2s)−(61)1/2px+(21)1/22py
- need to use x and y because of angle required
- π3(r)=(31)2(−2s)−(61)1/2px−(21)1/22py
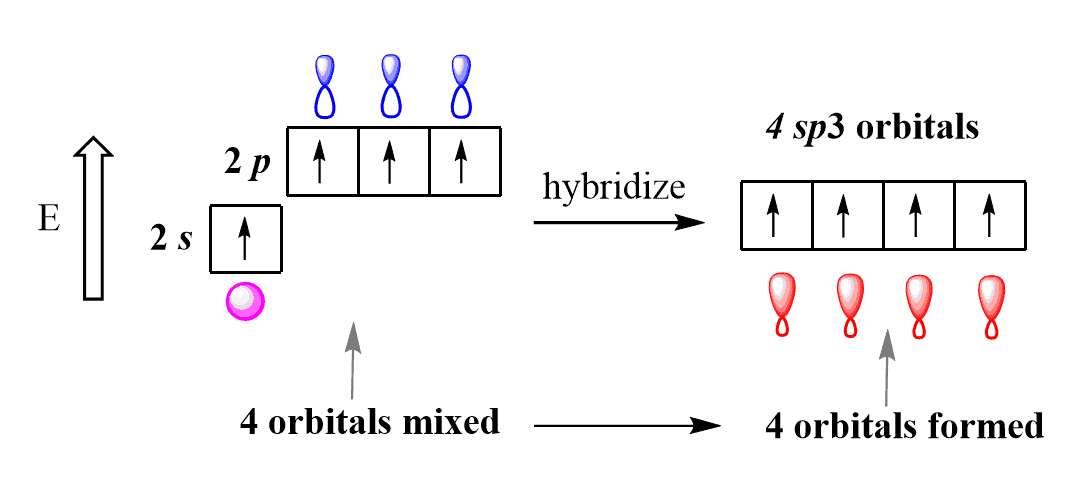
- CH4
- tetrahedral geo
- basis set: 2s,2px,2py,2pz
- π1(r)=−21(2s+2px+2py+2pz)→ 109.5 degree angle
- carbon can be described using sp,sp2,sp3 hybridization
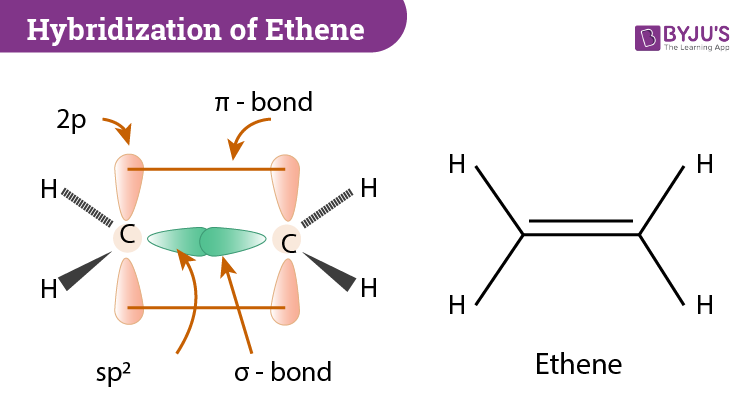
- C2H4
- sp2 hybridization b/c steric number of 3
- double bond ⟹ σ,π bond together
- non-hybridized p orbitals bond for π bond
- triple bond example: acetylene






